Theme: Public Awareness and Responsibilities regarding Health & Safety issues
Occupational Health-2017
Conference series LLC Conferences invites all the participants from all over the world to attend 6th International Conference and Exhibition on Occupational Health and Safety which will be held from September 13-14, 2017 at Dallas, USA. This program area is flexible and suited to both participants attending specific courses related to their immediate needs or those seeking a comprehensive Certificate Program in Occupational Health & Safety Management.
Occupational Health2017 will schedule and coordinate all meetings with our Editorial Board Members and other experts in the Research and Safety field across the World. The scientific program paves a way to gather visionaries through the research talks and presentations and put forward many thought provoking strategies on Occupational Health & Safety. Occupational Health main aim is to bring awareness in the people while working in their respective areas, make them learn how important the occupational therapy is and protect themselves from occupational diseases.
Conference series LLC Organizes 1000+ Global Events Every Year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific societies and Publishes 700+ Open access journals which contains over 100000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board and organizing committee members.
Track 1: Women Occupational Health
Identifying issues and problems in the occupational women health remains a challenge. Much of women's work remains anonymous, unpaid and uncounted such as in agriculture, food production and the marketing of home-made products and work in the home. Within the paid labor force, women are disproportionately focused in the informal sector, moreover the scope of industrial regulations, trade unions, insurance or even data collection. Women may undertake paid work at home, or part time or full time paid work with household work and the care of children, the sick and the elderly. They are inclined to move in and out of the paid labor force during distinct life stages; within the paid labor force they may have a variety of different jobs and occupations in succession.
Related Associations & Societies: British Occupational Hygiene Society, National Safety Management Society, American Association of Occupational Health Nurses, National Occupational Safety & Health Committee, Safety Health Association, Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety.
· Women Healthcare
· Physical activity of women
· Family Health
· Child Care
Track 2: Occupational Disease and Human Health
The ecumenical market for culled healthcare-acquired infection (HAI) treatments was valued at proximately $15.2 billion in 2014. This market is expected to increment from proximately $17.1 billion in 2015 to $23 billion by 2020, with a compound annual magnification rate (CAGR) of 6.1% from 2015 to 2020.
A word related infection is a sickness or issue that is brought on by the work or working conditions. This implies that the sickness probably grew because of exposures in the Workplace and that the relationship between the exposures and the infection is no doubt understood in therapeutic examination. Word related skin infections and conditions are for the most part brought on by chemicals and having wet hands for long stretches while at work. Skin inflammation is by a long shot the most well-known, yet urticarial, sunburn and skin disease are additionally of concern.
Risk occupations include:
Skin healthcare, Dental healthcare, Environmental contamination and health concerns, Biomarkers for human health, Efficacy and safety of drug use and Biosafety: Environment, health and safety, Hairdressing, Catering, Healthcare, Motor vehicle repair, Construction
· Occupational Asthma
· Occupational Dermatitis
· Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
· Occupational HIV infection
Track 3: Occupational Medicine and Therapy
In the course of recent years, the Occupational Therapists industry has developed, because of the expanding elderly populace obliging word related treatment for age-related infirmities. Moreover, a mental imbalance is the quickest developing improvement inability, which has helped patients interest for industry administrations to help with formative exercises, among other day by day errands. In the following five years, industry income is estimated, driven by the proceeded with interest from the elderly populace. The Occupational Therapists industry has a low level of capital power. In 2015, for each dollar spent on work, industry administrators are relied upon to burn through $0.04 on capital speculations.
Occupational therapy is the utilization of assessment and treatment to develop, recuperate, or maintain the circadian living and work skills of people with a physical, phrenic, or cognitive disorder. Occupational therapy additionally focuses much of their work on identifying and eliminating environmental barriers to independence and participation in daily activities. Word related treatment is a customer focused practice that places accentuation on the advancement towards the customer's objectives. Word related treatment mediations concentrate on adjusting nature, changing the assignment, showing the aptitude, and instructing the customer/family so as to expand investment in and execution of day by day exercises, especially those that are important to the customer. Occupational therapists often work proximately with professionals in physical therapy, verbalization therapy, nursing care, convivial work, and the community
Word related medication is the branch of clinical drug most dynamic in the field of word related wellbeing. OM authorities work to guarantee that the most noteworthy models of word related wellbeing and security can be accomplished and kept up. While it may include a wide number of orders, it focuses on the preventive pharmaceutical and administration of ailment, damage or inability that is identified with the working environment. This session also includes Physical and Biological stressors, Workplace amenities and first aid, Safe work method statements, Health and medical management, Industrial hygiene, Health psychology and Safety protection.
· Occupational Medicine Specialist
· Preventive Medicine
· Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation
· Occupational Health Psychology
· Occupational Health Epidemiology
· Occupational Health Physiotherapy
· Occupational Rehabilitation
Track 4: Occupational Hazards:
Hazardous waste sites pose a multitude of health and safety concerns, any one of which could result in serious injury or death. These hazards are a function of the nature of the site as well as a consequence of the work being performed. Several factors distinguish the hazardous waste site environment from other occupational situations involving hazardous substances. One important factor is the uncontrolled condition of the site. Even extremely hazardous substances do not endanger human health or safety if they are properly handled. However, improper control of these substances can result in a severe threat to site workers and to the general public. Another factor is the large variety and number of substances that may be present at a site. Any individual location may contain hundreds or even thousands of chemicals. Frequently, an accurate assessment of all chemical hazards is impossible due to the large number of substances and the potential interactions among the substances. In addition, the identity of the substances on site is frequently unknown, particularly in the initial stages of an investigation. The Project Team Leader will often be forced to select protective measures based on little or no information. Finally, workers are subject not only to the hazards of direct exposure, but also to dangers posed by the disorderly physical environment of hazardous waste sites and the stress of working in protective clothing.
· Chemical exposure.
· Fire and explosion.
· Oxygen deficiency.
· Ionizing radiation.
· Biologic hazards. ·
· Safety hazards.
· Electrical hazards.
· Heat stress.
· Cold exposure.
· Noise.
Track 5:
Risk Assessment
Modern occupational safety and health legislation usually demands that a risk assessment be carried out prior to making an intervention. It should be kept in mind that risk management requires risk to be managed to a level which is as low as is reasonably practical.
The calculation of risk is based on the likelihood or probability of the harm being realized and the severity of the consequences. This can be expressed mathematically as a quantitative assessment (by assigning low, medium and high likelihood and severity with integers and multiplying them to obtain a risk factor), or qualitatively as a description of the circumstances by which the harm could arise.
The assessment should be recorded and reviewed periodically and whenever there is a significant change to work practices. The assessment should include practical recommendations to control the risk. Once recommended controls are implemented, the risk should be re-calculated to determine if it has been lowered to an acceptable level. Generally speaking, newly introduced controls should lower risk by one level, i.e., from high to medium or from medium to low.
· Identify the hazards
· Identify all affected by the hazard and how
· Evaluate the risk
· Identify and prioritize appropriate control measures
Track 6: Occupational health services
It is desirable that some sort of occupational health services be established in every country. This may be done either by laws or regulations, or by collective agreements, or as otherwise agreed upon by the employers and workers concerned, or in any other manner approved by the competent authority after consultation with the representative organizations of employers and workers concerned. The coverage of workers by occupational health services varies widely, ranging from 5-10 per cent at best in the developing world up to 90 per cent in industrialized countries, especially those in Western Europe. There is therefore a universal need to increase worker coverage throughout the world. Ideally, each country should progressively develop occupational health services for all workers, including those in the public sector and members of production cooperatives, in all branches of economic activity and in all enterprises. The occupational health services provided should be adequate and appropriate to the specific health risks of the enterprises. These services should also include the necessary measures to protect self-employed persons and informal sector operators. To that end, plans should be drawn up to affect such measures and to evaluate progress made towards their implementation.
· Organization
· Functions
· Primary health care approach
· First aid
· Curative health services and rehabilitation
· Special occupational health needs
· Cooperation and coordination
Track 7: Current Issues in Occupational Health and Safety
The occupational safety and health status of the workforce is influenced by numerous variables; not least it’s changing analytical structure, the advancement of new technologies and a declination in the importance of economic sectors that initially dominated, such as industry and mining. This is bringing about transition not only in the numbers of jobs in every sector, but also the categories of jobs that are accessible. The workforce age profile is changing. New technologies are creating new league of employment.
Globalization implies that health threats that were once distant easily spread around the world in a short span. If these preserves the health of its workforce and manage its economic strength and its competitiveness, it needs to meet such challenges proactively. This Outlook provides an overview of the present and future patterns that are relevant to occupational health, the major workplace risks and their prevention.
Related Associations & Societies: Safety Health Association, British Occupational Hygiene Society, National Safety Management Society, American Association of Occupational Health Nurses, Occupational Health and Safety - American Public Health Association
· Occupational Stress
Track 8: Human factors and ergonomics
Human factors and ergonomics (commonly referred to as HF&E), also known as comfort design, functional design, and systems, is the practice of designing products, systems, or processes to take proper account of the interaction between them and the people who use them.
The field has seen some contributions from numerous disciplines, such as psychology, engineering, biomechanics, industrial design, physiology, and anthropometry. In essence, it is the study of designing equipment, devices and processes that fit the human body and its cognitive abilities. The two terms "human factors" and "ergonomics" are essentially synonymous.
The International Ergonomics Association defines ergonomics or human factors as follows:
Ergonomics (or human factors) is the scientific discipline concerned with the understanding of interactions among humans and other elements of a system, and the profession that applies theory, principles, data and methods to design in order to optimize human well-being and overall system performance.
HF&E is employed to fulfill the goals of occupational health and safety and productivity. It is relevant in the design of such things as safe furniture and easy-to-use interfaces to machines and equipment.
Proper ergonomic design is necessary to prevent repetitive strain injuries and other musculoskeletal disorders, which can develop over time and can lead to long-term disability.
Human factors and ergonomics is concerned with the "fit" between the user, equipment and their environments. It takes account of the user's capabilities and limitations in seeking to ensure that tasks, functions, information and the environment suit each user.
To assess the fit between a person and the used technology, human factors specialists or ergonomists consider the job (activity) being done and the demands on the user; the equipment used (its size, shape, and how appropriate it is for the task), and the information used (how it is presented, accessed, and changed). Ergonomics draws on many disciplines in its study of humans and their environments, including anthropometry, biomechanics, mechanical engineering, industrial engineering, industrial design, information design, kinesiology, physiology, cognitive psychology, industrial and organizational psychology, and space psychology.
· Building and Structure design
· Space Psychology
· Anthropometry
· Kinesiology
· Health Effects of Alcohol
· Industrial and organizational Psychology
Track 9: Agriculture Health and Safety
Agriculture workers are often at risk of work-related injuries, lung disease, noise-induced hearing loss, skin disease, as well as certain cancers related to chemical use or prolonged sun exposure. On industrialized farms, injuries frequently involve the use of agricultural machinery. The most common cause of fatal agricultural injuries in the United States is tractor rollovers, which can be prevented by the use of roll over protection structures which limit the risk of injury in case a tractor rolls over. Pesticides and other chemicals used in farming can also be hazardous to worker health, and workers exposed to pesticides may experience illnesses or birth defects. As an industry in which families, including children, commonly work alongside their families, agriculture is a common source of occupational injuries and illnesses among younger workers. Common causes of fatal injuries among young farm worker include drowning, machinery and motor vehicle-related accidents.
The 2010 NHIS-OHS found elevated prevalence rates of several occupational exposures in the agriculture, forestry, and fishing sector which may negatively impact health. These workers often worked long hours. The prevalence rate of working more than 48 hours a week among workers employed in these industries was 37% and 24% worked more than 60 hours a week. Of all workers in these industries, 85% frequently worked outdoors compared to 25% of all U.S. workers. Additionally, 53% were frequently exposed to vapors, gas, dust, or fumes, compared to 25% of all U.S. workers.
· Toxicology.
· Pollution Research
· Biosafety
· Environmental Health and Engineering.
Track 10: Chronic Health, Industrial Food Safety and Management
Incessant sicknesses constitute a noteworthy reason for mortality and the World Health Organization (WHO) reports interminable non-transmittable conditions to be by a wide margin the main reason for mortality on the planet, speaking to 35 million passing in 2005 and more than 60% of all passing.
The sustenance security testing business sector is anticipated to reach $15,040.7 million by 2019. In 2013, the business sector was overwhelmed by North America, trailed by Europe. The Asia-Pacific business sector is anticipated to develop at the most astounding CAGR amid the gauge period.
An incessant condition is a human wellbeing condition or infection that is tireless or generally durable in its belongings or a sickness that accompanies time. The term unending is normally connected when the course of the sickness goes on for over three months. Normal ceaseless ailments incorporate joint pain, asthma, tumor, COPD, diabetes and viral sicknesses, for example, hepatitis C and HIV/AIDS.
Sustenance security is an investigative control portraying taking care of, planning, and stockpiling of nourishment in ways that avert foodborne sickness. This incorporates various schedules that ought to be taken after to maintain a strategic distance from conceivably extreme wellbeing dangers. The tracks inside of this line of believed are wellbeing in the middle of industry and the business and afterward between the business sector and the shopper. In considering industry to market rehearses, nourishment wellbeing contemplations incorporate the roots of sustenance including the works on identifying with sustenance naming, nourishment cleanliness, nourishment added substances and pesticide deposits, and in addition strategies on biotechnology and sustenance and rules for the administration of administrative import and fare review and certificate frameworks for nourishments.
An aliment safety risk analysis is essential not only to engender or manufacture high quality goods and products to ascertain safety and forfend public health, but withal to comply with international and national standards and market regulations. With risk analyses victuals safety systems can be fortified and victuals-borne illnesses can be reduced. Victuals safety risk analyses fixate on major safety concerns in manufacturing premises—not every safety issue requires a formal risk analysis. Sometimes, especially for involute or controversial analyses, customary staff is fortified by independent consultants. This session includes temporomandibular problem, Rheumatoid arthritis, Spinal stenosis, Food safety- Standards & regulations, Food quality control and safety measures- Consumer labeling, Food safety, Risk assessment and management, Food toxicology and microbiology-Spoilage prevention and control and Novel methods for the evaluation of food adulteration and authenticity.
Occupational Health 2017 welcomes attendees, presenters, and exhibitors from all over the world to Dallas, Texas, USA. We are delighted to invite you all to attend and register for the “6thInternational Conference and Exhibition on Occupational Health and Safety (Occupational Health-2017)” which is going to be held during September 13-14, 2017 in Dallas, Texas, USA.
The organizing committee is gearing up for an exciting and informative conference program including plenary lectures, symposia, workshops on a variety of topics, poster presentations and various programs for participants from all over the world. We invite you to join us at the Occupational Health-2017, where you will be sure to have a meaningful experience with scholars from around the world. All members of the Occupational Health-2017 organizing committee look forward to meeting you in Dallas, Texas, USA. For more details please visit- http://occupationalhealth.conferenceseries.com/
Scope & Importance:
Occupational safety and health (OSH) relates to safety health issues at work environment. Occupational health relates to all environmental diseases. It provides that employers maintain plants and systems that are reasonably and practicably safe; they ensure safe methods of handling, storing and transporting materials and also provide adequate induction, training and supervision in those methods. This program area is flexible and suited to both participants attending specific courses related to their immediate needs or those seeking a comprehensive Certificate Program in Occupational Health & Safety Management.
Occupational health will aim for the promotion and maintenance of the highest degree of physical, mental and social well-being of workers in all occupations. Mostly the prevention and protection amongst workers of departures from health caused by their working conditions and their employment from risks resulting from factors adverse health. The workers in an occupational environment adapted to his physiological and psychological capabilities. The main goal of this program is to provide safety awareness along with demonstration of advance safety equipment’.
Why Dallas?
Dallas is a major city in Texas and is the largest urban center of the fourth most populous metropolitan area in the United States. The city proper ranks ninth in the U.S. and third in Texas after Houston and San Antonio. The city's prominence arose from its historical importance as a center for the oil and cotton industries, and its position along numerous railroad lines. The bulk of the city is in Dallas County, of which it is the county seat; however, sections of the city are located in Collin, Denton, Kaufman, and Rockwall counties.
Dallas is centrally located and within a four-hour flight from most North American destinations. DFW International Airport is the world's fourth busiest airport, offering nearly 1,750 flights per day and providing non-stop service to 145 domestic and 47 international destinations worldwide annually. In addition, Dallas Love Field Airport is conveniently located 10 minutes from downtown. Once here, visitors can ride DART, one of the fastest-growing light rail systems in the nation or the historic, free McKinney Avenue Trolley from the Dallas Arts District throughout the Uptown area with its restaurants, pubs, boutique hotels and shops.
Throughout the city, a visitor will enjoy the best shopping in the southwest, four-and five-diamond/star hotels and restaurants, the largest urban arts district in the nation, 14 entertainment districts and much more. Blend in moderate weather, year-round sports and true Southern hospitality for a true "taste" of the Dallas difference. Visitors are exposed to a city of success ... where optimism meets opportunity. Its pioneering spirit is alive and well, and the philanthropic contributions from its many residents continue to enrich the community and quality of life.
Conference Highlights:
- Women Occupational Health
- Occupational Disease and Human Healthy
- Occupational Medicine and Therapy
- Occupational Hazards
- Risk Assessment
- Occupational health services
- Current Issues in Occupational Health and Safety
- Human factors and ergonomics
- Agriculture Health and Safety
- Chronic Health, Industrial Food Safety and Management
Target Audience:
Professors, Associate Professors, Assistant Professors, PhD Scholars, Graduates and Post Graduates, Directors, CEO’s of Organizations, Association, Association presidents and professionals, Noble laureates in Health Care and Medicine, Research Institutes and members, Supply Chain companies, Manufacturing Companies, Training Institutes, Business Entrepreneurs
Target Audience:
Industry 30%
Academia 60%
Others 10%
Major Associations around the Globe
- WHO
- American College of Occupational and Environmental Medicine
- Society of Occupational Medicine
- Industrial Hygiene Association
- Alberta Construction Safety Association
- British Safety Industry Federation (BSIF)
- Nova Scotia Construction Safety Association
Major Associations in USA
- American Occupational Therapy Association
- Safety Health Associations
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration
- Central California Safety Council
- Orange County California Association of Occupational Health Nurses
- California State Association of Occupational Health Nurses
Top Universities in USA:
- Princeton University
- Harvard University
- Yale University
- Columbia University
- Stanford University
- University of Baltimore
Potential Growth Areas in OHS
- Agriculture, Forestry, and Fishing
- Construction
- Health Care and Social Assistance
- Manufacturing
- Mining
- Oil and Gas Extraction
- Public Safety
- Services
- Transportation, Warehousing, and Utilities
- Wholesale and Retail Trade
Potential Growth Areas in Occupational Health
Capital expenditures by sector, by province and territory ($millions)
Medicare Home Health and Hospice care Revenue:
Market Value of Healthcare in USA:
Health care costs continue to rise in the U.S. and throughout the developed world. Total U.S. health care expenditures were estimated to be $3.09 trillion in 2014, and are projected to soar to $3.57 trillion in 2017.The health care market in the U.S. in 2014 included the major categories of hospital care ($959.9 billion), physician and clinical services ($618.5 billion), dental services ($122.4 billion) and prescription drugs ($290.7 billion), along with nursing home and home health care ($248.5 billion). Registered U.S. hospitals totaled 5,723 properties in 2012, according to an American Hospital Association survey, containing 920,829 beds serving 36.1 million admitted patients during the year.
Market Value of Healthcare in World:
Healthcare investment in more than 30 nations including the majority of the world’s most developed economies (but excluding Brazil, Russia, India or China), found stark contrasts between health costs in the United States and those of other nations. In 2012 (the latest complete data available), the average of a list that includes, for example, the UK, France, Germany, Mexico, Canada, South Korea, Japan, Australia and the U.S., spent 9.3% of GDP on health care, unchanged from the previous year. The highest figures in this study were in America at 16.9% of GDP, The Netherlands at 11.9%, France at 11.6%, Switzerland at 11.4%, Germany at 11.3%, Austria at 11.1%, Denmark at 11.0% and Canada at 10.9%.
Growth by next 5-10 years in Worldwide:
The number of seniors covered by Medicare will continue to grow at an exceedingly high rate, from 47.4 million people in 2010 to 81.4 million in 2030. Health informatics industry is expected to reach the value of $6.5 billion by the year 2012 owing to the increase in level of adoption of clinical informatics networks. The number of hospitals adopting the electronic health record (EHR) systems for monitoring and recording the health related data of patients is growing day by day. First being the increasing use of EMRs and EHRs by medical professionals for improving the quality of their services and second being reduction in operating costs of hospitals and related healthcare facilities in near future. The US market for EMRs was estimated at $2.18 billion in 2009 which is forecasted to rise to $6.05 billion by the year 2015 at the compounded annual growth rate of 18.1% during the forecast period from 2010 to 2015.
Fund Allotment to Healthcare Research in USA:
The NIH invests nearly $30.3 billion annually in medical research for the American people. More than 80% of the NIH's funding is awarded through almost 50,000 competitive grants to more than 300,000 researchers at more than 2,500 universities, medical schools, and other research institutions in every state and around the world. About 10% of the NIH's budget supports projects conducted by nearly 6,000 scientists in its own laboratories, most of which are on the NIH campus in Bethesda, Maryland.
Fund Allotment to Healthcare Research in World:
The Welcome Trust is the UK's largest non-governmental source of funds for biomedical research and provides over £600 million per year in grants to scientists and funds for research centres. In the United States, in 2003 about 94 billion dollars were provided for biomedical research in the United States. The National Institutes of Health and pharmaceutical companies collectively contribute 26.4 billion dollars and 27.0 billion dollars, respectively, which constitute 28% and 29% of the total, respectively. Other significant contributors include biotechnology companies (17.9 billion dollars, 19% of total), medical device companies (9.2 billion dollars, 10% of total), other federal sources, and state and local governments. Foundations and charities, led by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, contributed about 3% of the funding. In Australia, in 2000/01, about $1.7B was spent on biomedical research, with just under half ($800M, 47%) sourced from the Commonwealth government. About $540M came from business investments/funding and a further $220M from private or not-for-profit organizations (totaling 44%). The balance was from state and local governments. Since then there has been a significant in government funding through the National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC), whose expenditure on research was nearly $700 million in 2008–09.
Occupational Health 2017 welcomes attendees, presenters, and exhibitors from all over the world to Dallas, Texas, USA. We are delighted to invite you all to attend and register for the “6thInternational Conference and Exhibition on Occupational Health and Safety (Occupational Health-2017)” which is going to be held during September 13-14, 2017 in Dallas, Texas, USA.
The organizing committee is gearing up for an exciting and informative conference program including plenary lectures, symposia, workshops on a variety of topics, poster presentations and various programs for participants from all over the world. We invite you to join us at the Occupational Health-2017, where you will be sure to have a meaningful experience with scholars from around the world. All members of the Occupational Health-2017 organizing committee look forward to meeting you in Dallas, Texas, USA. For more details please visit- http://occupationalhealth.conferenceseries.com/
Scope & Importance:
Occupational safety and health (OSH) relates to safety health issues at work environment. Occupational health relates to all environmental diseases. It provides that employers maintain plants and systems that are reasonably and practicably safe; they ensure safe methods of handling, storing and transporting materials and also provide adequate induction, training and supervision in those methods. This program area is flexible and suited to both participants attending specific courses related to their immediate needs or those seeking a comprehensive Certificate Program in Occupational Health & Safety Management.
Occupational health will aim for the promotion and maintenance of the highest degree of physical, mental and social well-being of workers in all occupations. Mostly the prevention and protection amongst workers of departures from health caused by their working conditions and their employment from risks resulting from factors adverse health. The workers in an occupational environment adapted to his physiological and psychological capabilities. The main goal of this program is to provide safety awareness along with demonstration of advance safety equipment’.
Why Dallas?
Dallas is a major city in Texas and is the largest urban center of the fourth most populous metropolitan area in the United States. The city proper ranks ninth in the U.S. and third in Texas after Houston and San Antonio. The city's prominence arose from its historical importance as a center for the oil and cotton industries, and its position along numerous railroad lines. The bulk of the city is in Dallas County, of which it is the county seat; however, sections of the city are located in Collin, Denton, Kaufman, and Rockwall counties.
Dallas is centrally located and within a four-hour flight from most North American destinations. DFW International Airport is the world's fourth busiest airport, offering nearly 1,750 flights per day and providing non-stop service to 145 domestic and 47 international destinations worldwide annually. In addition, Dallas Love Field Airport is conveniently located 10 minutes from downtown. Once here, visitors can ride DART, one of the fastest-growing light rail systems in the nation or the historic, free McKinney Avenue Trolley from the Dallas Arts District throughout the Uptown area with its restaurants, pubs, boutique hotels and shops.
Throughout the city, a visitor will enjoy the best shopping in the southwest, four-and five-diamond/star hotels and restaurants, the largest urban arts district in the nation, 14 entertainment districts and much more. Blend in moderate weather, year-round sports and true Southern hospitality for a true "taste" of the Dallas difference. Visitors are exposed to a city of success ... where optimism meets opportunity. Its pioneering spirit is alive and well, and the philanthropic contributions from its many residents continue to enrich the community and quality of life.
Conference Highlights:
- Women Occupational Health
- Occupational Disease and Human Healthy
- Occupational Medicine and Therapy
- Occupational Hazards
- Risk Assessment
- Occupational health services
- Current Issues in Occupational Health and Safety
- Human factors and ergonomics
- Agriculture Health and Safety
- Chronic Health, Industrial Food Safety and Management
Target Audience:
Professors, Associate Professors, Assistant Professors, PhD Scholars, Graduates and Post Graduates, Directors, CEO’s of Organizations, Association, Association presidents and professionals, Noble laureates in Health Care and Medicine, Research Institutes and members, Supply Chain companies, Manufacturing Companies, Training Institutes, Business Entrepreneurs
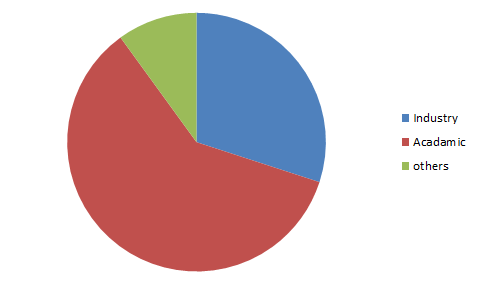
Target Audience:
Industry 30%
Academia 60%
Others 10%
Major Associations around the Globe
- WHO
- American College of Occupational and Environmental Medicine
- Society of Occupational Medicine
- Industrial Hygiene Association
- Alberta Construction Safety Association
- British Safety Industry Federation (BSIF)
- Nova Scotia Construction Safety Association
Major Associations in USA
- American Occupational Therapy Association
- Safety Health Associations
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration
- Central California Safety Council
- Orange County California Association of Occupational Health Nurses
- California State Association of Occupational Health Nurses
Top Universities in USA:
- Princeton University
- Harvard University
- Yale University
- Columbia University
- Stanford University
- University of Baltimore
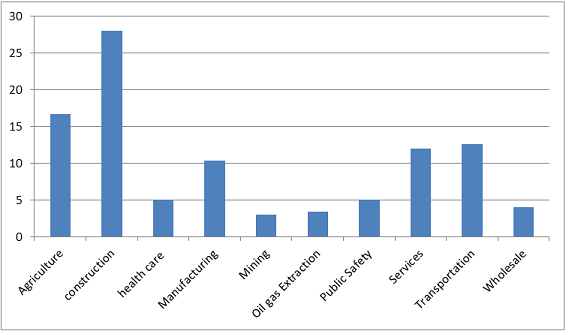
Potential Growth Areas in OHS
- Agriculture, Forestry, and Fishing
- Construction
- Health Care and Social Assistance
- Manufacturing
- Mining
- Oil and Gas Extraction
- Public Safety
- Services
- Transportation, Warehousing, and Utilities
- Wholesale and Retail Trade
Potential Growth Areas in Occupational Health
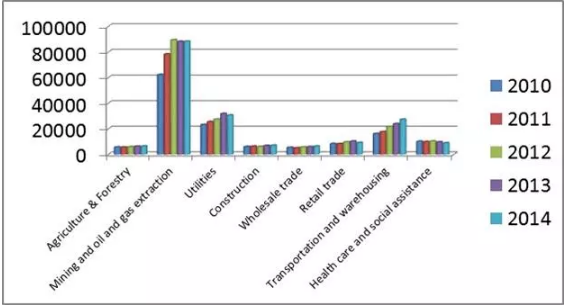
Capital expenditures by sector, by province and territory ($millions)
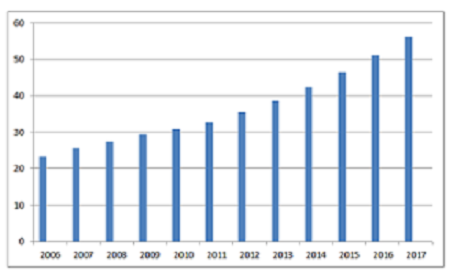
Medicare Home Health and Hospice care Revenue:
Market Value of Healthcare in USA:
Health care costs continue to rise in the U.S. and throughout the developed world. Total U.S. health care expenditures were estimated to be $3.09 trillion in 2014, and are projected to soar to $3.57 trillion in 2017.The health care market in the U.S. in 2014 included the major categories of hospital care ($959.9 billion), physician and clinical services ($618.5 billion), dental services ($122.4 billion) and prescription drugs ($290.7 billion), along with nursing home and home health care ($248.5 billion). Registered U.S. hospitals totaled 5,723 properties in 2012, according to an American Hospital Association survey, containing 920,829 beds serving 36.1 million admitted patients during the year.
Market Value of Healthcare in World:
Healthcare investment in more than 30 nations including the majority of the world’s most developed economies (but excluding Brazil, Russia, India or China), found stark contrasts between health costs in the United States and those of other nations. In 2012 (the latest complete data available), the average of a list that includes, for example, the UK, France, Germany, Mexico, Canada, South Korea, Japan, Australia and the U.S., spent 9.3% of GDP on health care, unchanged from the previous year. The highest figures in this study were in America at 16.9% of GDP, The Netherlands at 11.9%, France at 11.6%, Switzerland at 11.4%, Germany at 11.3%, Austria at 11.1%, Denmark at 11.0% and Canada at 10.9%.
Growth by next 5-10 years in Worldwide:
The number of seniors covered by Medicare will continue to grow at an exceedingly high rate, from 47.4 million people in 2010 to 81.4 million in 2030. Health informatics industry is expected to reach the value of $6.5 billion by the year 2012 owing to the increase in level of adoption of clinical informatics networks. The number of hospitals adopting the electronic health record (EHR) systems for monitoring and recording the health related data of patients is growing day by day. First being the increasing use of EMRs and EHRs by medical professionals for improving the quality of their services and second being reduction in operating costs of hospitals and related healthcare facilities in near future. The US market for EMRs was estimated at $2.18 billion in 2009 which is forecasted to rise to $6.05 billion by the year 2015 at the compounded annual growth rate of 18.1% during the forecast period from 2010 to 2015.
Fund Allotment to Healthcare Research in USA:
The NIH invests nearly $30.3 billion annually in medical research for the American people. More than 80% of the NIH's funding is awarded through almost 50,000 competitive grants to more than 300,000 researchers at more than 2,500 universities, medical schools, and other research institutions in every state and around the world. About 10% of the NIH's budget supports projects conducted by nearly 6,000 scientists in its own laboratories, most of which are on the NIH campus in Bethesda, Maryland.
Fund Allotment to Healthcare Research in World:
The Welcome Trust is the UK's largest non-governmental source of funds for biomedical research and provides over £600 million per year in grants to scientists and funds for research centres. In the United States, in 2003 about 94 billion dollars were provided for biomedical research in the United States. The National Institutes of Health and pharmaceutical companies collectively contribute 26.4 billion dollars and 27.0 billion dollars, respectively, which constitute 28% and 29% of the total, respectively. Other significant contributors include biotechnology companies (17.9 billion dollars, 19% of total), medical device companies (9.2 billion dollars, 10% of total), other federal sources, and state and local governments. Foundations and charities, led by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, contributed about 3% of the funding. In Australia, in 2000/01, about $1.7B was spent on biomedical research, with just under half ($800M, 47%) sourced from the Commonwealth government. About $540M came from business investments/funding and a further $220M from private or not-for-profit organizations (totaling 44%). The balance was from state and local governments. Since then there has been a significant in government funding through the National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC), whose expenditure on research was nearly $700 million in 2008–09.
Conference Highlights
- Occupational Women Health
- Occupational Disease and Human Health
- Occupational Medicine and Therapy
- Agriculture Health and Safety
- Chronic Health, Industrial Food Safety and Management
- Risk Assessment
- Occupational Hazards
- Occupational Health assistance
- Prevailing Issues in Occupational Health and Safety
- Human factors and ergonomics
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | September 13-14, 2017 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | Day 1 | Day 2 | |
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
- Occupational Medicine & Health Affairs
- Journal of Ergonomics
- International Journal of Public Health and Safety
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by































